Overview
The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has established the National Certification System for Tissue Culture Raised Plants (NCS-TCP) (https://dbtncstcp.nic.in/) through a Gazette Notification of the Ministry of Agriculture dated March 10, 2006. This program promotes Agri-entrepreneurship and safeguards farmers’ interests by providing a certification system for virus-free and true-to-type tissue culture-raised plants of various crops. The DBT has established a well-defined operational structure for the successful implementation of NCS-TCP in India.
The major challenge for the success of the tissue culture industry is controlling the infection of plants by fastidious pathogens such as viruses, viroids, and phytoplasmas while maintaining the genetic uniformity of crops.
The vision of this scientific program is to revolutionize the tissue culture industry by ensuring a stringent system for the propagation and distribution of virus-free and genetically uniform plants. The mission is to enhance agricultural productivity and sustainability by controlling plant infections caused by pathogens such as viruses, viroids, and phytoplasmas.
The program’s mandate is to enforce standard practices for tissue culture and certify the complying tissue culture plant facilities thereby minimizing the spread of pathogens and ensuring high-quality plant production. This involves rigorous research and development, quality control, and implementation of best practices in plant tissue culture.
The main objectives of the program include:
- Develop and standardize protocols to control infections caused by fastidious pathogens, ensuring the production of healthy tissue culture plants.
- Maintain the genetic uniformity of tissue culture-raised crops to ensure consistency and reliability in agricultural production.
- Propagate and distribute virus-free, high-quality tissue culture plants to growers and farmers, enhancing agricultural productivity.
- Promote and support research and development activities in plant tissue culture to innovate and improve existing techniques and methodologies.
- Facilitate the commercialization of the plant tissue culture industry in India, catering to local needs, and export demands, and contributing to the growth of the agricultural sector.
Recent initiatives and activities:
- Recognized and new companies have been offered substantial support. In 2023, nine new companies were recognized, and 15 applications are under process for recognition in 2024. This initiative aims to expand and strengthen the tissue culture industry.
- Regular meetings with recognized companies are conducted to encourage testing and address any issues they face. This proactive engagement has resulted in a phenomenal 82% increase in plant testing over the last two years.
- The introduction of QR codes on certificate labels has enhanced traceability, providing all relevant information such as the source of the crop and the ATL where it was tested. This initiative ensures transparency and quality assurance in the tissue culture industry.
- The NCSTCP Management Cell closely monitors the disposal of virus-infected plants, ensuring that these plants do not reach farms and thereby maintaining the health and quality of agricultural produce.
- Webinars have been introduced to raise awareness about the transformative potential of the tissue culture industry in Indian agriculture. These webinars serve as a platform for sharing knowledge, technology, and innovation, benefiting stakeholders.
- Targeted outreach awareness programs have been conducted to expand the program and improve awareness of stakeholders. These programs aim to educate and engage farmers, researchers, and industry professionals about the benefits and advancements in tissue culture.
- A new website (https://dbtncstcp.nic.in/) and portal (https://dynamic.dbtncstcp.nic.in/#/login) have been developed to enhance user experience and operational efficiency for the NCSTCP. This digital initiative aims to provide a user-friendly interface and improved functionality, facilitating better access to information and services.
Notable outcomes/achievements of the program:
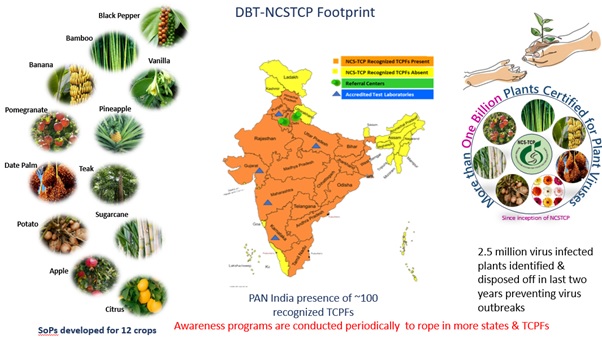
100 Tissue Culture Propagation Facilities (TCPFs) have been recognized so far out of which 9 new companies have joined the program spanning 17 states showing the program’s strong nationwide presence. Through consistent monitoring and support, testing of plants has witnessed an impressive 82% increase from 2021 to 2023. A staggering 189,255 TCPs, representing over 176 million plants across various crops (apple, bamboo, banana, date palm, gerbera, potato, sugarcane), were tested for virus indexing and genetic fidelity. Comprehensive virus indexing was conducted on over 44,612 mother plants/stock cultures (MP/SC) across various crops. Certificates of Quality were issued for all tested plants, and 25,460 certificate labels were awarded to TCPs confirmed virus-free and genetically uniform. A critical outcome of these activities is the identification and exclusion of over 1.6 million virus-infected plants, preventing them from reaching farms. Further, nine informative webinars and two
physical awareness programs were organized. These webinars covered a diverse range of crops, from fruits to ornamentals, while also addressing crucial topics like virus indexing and quarantine procedures. Two awareness programs were held specifically in the northeastern states of Sikkim and Assam, reaching over 100 participants each. Besides these, a new user-friendly website and portal were launched to streamline information access and functioning of the NCSTCP. These achievements demonstrate a strong commitment to safeguarding plant health and supporting the production of high-quality crops.
The tissue culture program has had a profound impact on society, particularly in the agricultural sector. One of the major crops benefiting from this program is banana, which constitutes approximately 85% of all the crops under this initiative. Farmers using virus-free, healthy tissue culture plants experienced up to 30% increase in yield. This translates to higher incomes and improved livelihoods. Government of India data reveals a remarkable 8-fold increase in banana exports over the past decade. This robust export market creates opportunities for farmers to tap into global markets. Many TCPFs are located in remote areas, employing the local rural population. It has been observed that more than 50% of the workforce in these facilities are women. This employment injects income into rural communities, leading to an improved standard of living. In summary, the tissue culture program is not only enhancing agricultural productivity and quality but is also playing a crucial role in socio-economic development. By increasing farmers' incomes, boosting exports, and generating rural employment, the program is contributing significantly to the overall betterment of society.
Contacts Concerned Officer for more Information
| Programme Head | Dr. Nitin Kumar Jain, Scientist G |
|---|---|
| nitink[dot]jain[at]nic[dot]in | |
| Phone No. | 011-24365972 |
| Programme Officer | Phone No. | |
|---|---|---|
| Dr. Manoj Kumar Modi, Scientist F | manoj[dot]modi[at]nic[dot]in | 011-24369383 |