Public Health & Nutrition
Vision: To develop technological and clinical solutions for the Public Health Nutrition related problems like malnutrition, anemia, stunting etc.
Objectives:Addressal of micronutrient & macronutrient deficiencies, severe acute malnutrition, Stunting, Agri-nutrition linkages, food fortification, over nutrition, probiotics for human health and well-being, food safety, molecular detection of GM traits in foods, development of low cost foods/ supplements and utilization of agricultural residues for value added products and capacity building in Food Science and Nutrition Biology.
Some of the key questions being addressed are:
- Why are so many women and children anemic?
- Why are so many children still stunted?
- Why are so many babies born small?
Initiatives and Programmes supported:
Addressal of MN Deficiencies; Maternal and Child Nutrition; Geriatric Nutrition, Agri-Nutrition Linkages consist of the major initiatives over the past few years
Major Ongoing programmes:
An efficacy study to test the effectiveness of Fe-Vitamin B12 and Folate fortified rice in improving the iron stores and Hb in school children and their mothers in Koppal district of Karnataka has been initiated. Implementing partners are St.Johns Bangalore and IIT- Kharagpur. The fortified rice premix was indigenously developed by IIT-Kharagpur through DBTs support.
Agri-Nutrition Linkages for improvement of protein content in cereals:
- 30 mega varieties and high protein content rice lines are being tested for their protein/amino acid content and bioavailability/digestibility to come up with better rice variety to address the protein-energy malnutrition. This multi-institutional program would identify metabolic, physiological and genetic factors that restrict yield while selecting for high grain protein content in rice grains. It is envisaged to deploy accrued knowledge on genomic and other omic strategies to deliver a high yielding and high grain protein rice variety.
- Analysis of 15000 rice lines for protein content, protein composition and amino acid composition to understand the genetic and metabolic regulation of digestible protein quality and quantity
Fortified Wheat Nutritional Improvement: High resolution QTL mapping for iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), grain protein, and phytate content and their introgression in high yielding wheat cultivars has been initiated in NABI Mohali for the development of Improved wheat lines with high level of micronutrient (> 2 fold), Grain protein content (>15%), reduced level of anti-nutritional factor (>40% reduction), anti-oxidants (anthocyanin: > 2 fold), high level of amylose (>50%) &resistant starch (>15%).
Salient Achievements:
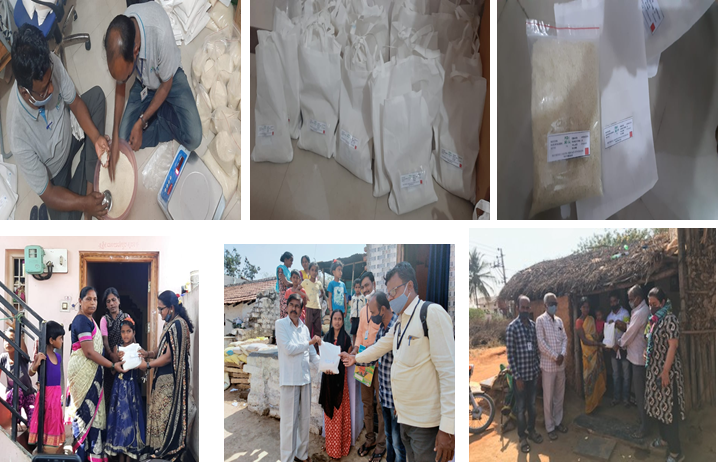
- Technology developed for iron, B12 and folic acid fortified rice. A pilot scale demonstration unit with 100 kg/day capacity, was designed and developed according to GMP and GLP norms by IIT Kharagpur.

Iron Fortified rice pre-mix
Distribution of Rice
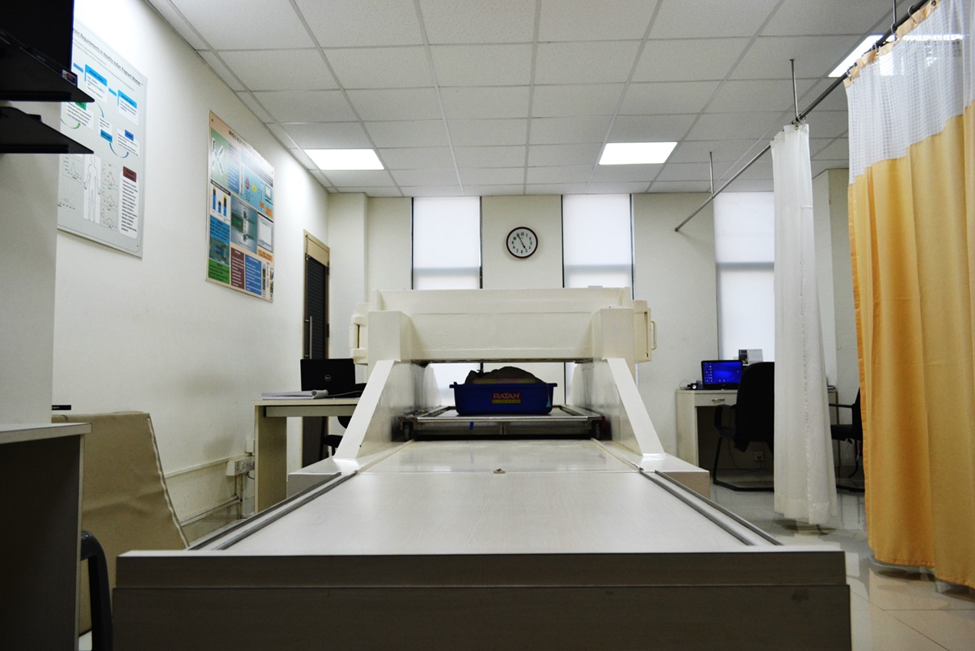
- Protein requirements for Indian pregnant women have been estimated using the whole-body potassium counter at SJRI and the findings published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, and these have been used to inform the ICMR-NIN requirements and the Poshan Abhiyaan
The picture above depicts a newborn baby being measured in the shadow-shield (the white structure) whole-body potassium counter: the baby lies in a cradle directly below the counting crystals, located in the shielded white box above.
- DBT developed simple, easily dispersible & cheap Zinc tablets for the National Public Health Programmes
- Iron Fortified Wheat Flour for anaemia addessal
- Development of DNA barcode and multiplex PCR based diagnostics for detection of nationally important seed borne fungal pathogens
Women and Child Health
Overview
The Women and Child Health programme was earlier known as the Maternal and Child Health Programme. It has been rechristened as the overall mandate of the program has expanded to include initiatives for addressing various problems encompassing women’s health. It is an important priority area for the country’s health needs and also in line with the Sustainable development goals of ensuring good health and well being. Several initiatives have been taken for advancing research and scientific knowledge in this area which encompass research from preconception to adolescence. Programmes have been supported on aspects of pregnancy complications, mechanistic paradigm governing the outcomes of pregnancy, congenital anomalies, diseases of neonatal period and early childhood. Several collaborative efforts have been initiated for hypothesis driven original research for answering questions relevant to our health need in the area.
Mandate
- Mechanistic paradigms underlying:
- Complications during pregnancy such as preeclampsia, preterm birth, IUGR, auto- immunity etc.
- Foetal growth & development, premature or abnormal birth, still birth, congenital anomalies etc., enabling research on developmental disorders including neurological disorders like CP and autism
- Gene (dys)function leading to early developmental anomalies & Gene environment interactions in the conditions mentioned above
- Problems encompassing women’s health including infections, autoimmune diseases exclu- sive to or more prevalent in women.
- Menopause and potential association with bone health and osteoporosis, implications of menstrual hygiene on reproductive health and management of menstrual wastes.
- Cancers exclusive to women and those resulting from deranged menstrual cycle.
- Developmental basis of adult onset of disease perspective including the effect of maternal and child malnutrition on the physical and cognitive development.
- Novel tools of prediction, early & easier disease detection and therapeutic intervention in the above conditions.
- In vivo, In vitro and AI based model system to study aspects of women's health and early development.
Thrust Areas
The present thrust areas of research under the Women and Child Health programme include Preterm birth, Neonatal Sepsis, Developmental disorders and diseases of infancy and early childhood, Placental Biology, Problems encompassing Women’s Health and Developmental basis of adult onset of disease.
Major Programs and Achievements
1. Pediatric Renal Biology Program Research on Nephrotic Syndrome
The chief achievements of this network proposal have been the creation of a platform for collaborative studies for nationwide investigators, establishing longitudinal cohorts of patients who are offered enrolment into prospective observational and interventional studies, and a well phenotyped biorepository that is a valuable resource for studies into disease pathogenesis. In collaboration with IIT Roorkee, an application (UTSARJAN) for remote monitoring of patient clinical status has been created and launched. The application enhances better parental involvement in the management of nephrotic syndrome
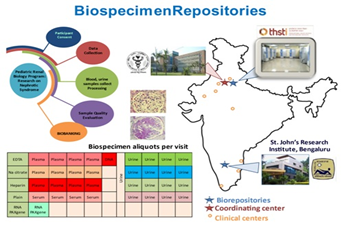
Figure 1: Biorepository (Nephrotic Syndrome)
2. Healthy Life Trajectories Initiative (HeLTI): Early Interventions to Support Trajectories for Healthy Life in India (EINSTEIN)
The Healthy Life Trajectories Initiative (HeLTI) was launched as a joint initiative between Canada, India, China and South Africa in collaboration with the World Health Organization to address the increasing burden of Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) – including obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease.
In the Indian part of the study set in rural Mysore called HeLTI EINSTEIN (Early Interventions to Support Trajectories for Healthy Life in India), women of reproductive age will receive a longitudinal multi-faceted intervention comprising of multiple micronutrients; a group parenting program; hygiene and infection prevention measures; and reduction of environmental pollution exposure.
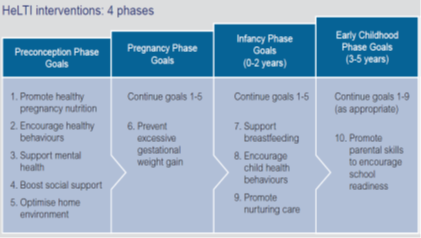
Figure 2: HeLTi interventions
So far, extensive formative work and harmonization across country sites has been carried out. The target villages have been mapped and enumerated; Eligible women and those who would be potentially eligible over the next year or so have been identified. The recruitment of participants and collection of baseline data is underway.
3. Inter-Institutional Program for Maternal, Neonatal and Infant Sciences: A translational approach to studying preterm birth (PTB)
GarbhINI: Inter discisplinary Group for Advanced Research on BirtH outcomes -DBT India Initiative
Preterm Birth is a complex syndrome with multiple etiologies that include interacting biological, psychosocial, and environmental factors. An inter-institutional and interdisciplinary programme was established in 2014 by the Department of Biotechnology with the ultimate objective to acquire deep fundamental knowledge about preterm birth and to use this knowledge to find efficient and sustainable solutions to reduce the associated morbidity and mortality. Under this program, a cohort of pregnant women known as the GARBH-INI Cohort was established in May 2015 at the Civil hospital in Gurugram (GCH), Haryana, India.
In the phase I of this programme, more than 27000 women were screened and a unique pregnancy cohort comprising more than 8000 women established using an interdisciplinary approach comprising methodologies of clinical, epidemiological, statistical, genetic, proteomic and imaging sciences. The GARBH-Ini platform comprises of a biorepository of well characterized clinical phenotypes with around 1 million bio-specimens and ~600,000 ultrasound images.
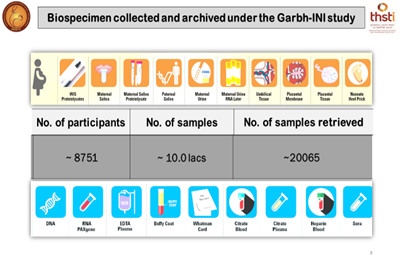
Figure 3: Garbhini Cohort and Biobank
The study so far has provided some valuable insights:
- In the cohort, the frequency of preterm birth has been found to be 13%, with high rates of other adverse birth outcomes. In addition to the well-known risk factors like prior PTB, short IP interval and short cervix at 3rd trimester, some less reported factors such as biomass fuel use and passive smoking as risk factors of Preterm birth have been identified. Interestingly, 9.5% of all PTBs in the cohort study could be attributed to exposure to indoor air pollution
- India – specific models of gestational age estimation have been developed with improved accuracy over the Hadlock& INTERGROWTH-21st models.
Phase II of the GARBH-Ini program is being supported to continue the efforts for acquiring deep fundamental knowledge about PTB and find efficient and sustainable solutions for the gamut of problems associated with preterm birth.
4. DBT Programme Support for Fetal Programming Research
This is a longitudinal study based on the Pune Maternal Nutrition Study (PMNS) and Pune Rural Intervention in Young Adolescents (PRIYA), to test the hypothesis that intervention with vitamin B12, multi micronutrients and protein in adolescent girls from before conception will favorably influence fetal programming of ‘diabesity’ in the offspring.
The results support the primary hypothesis that pre-conceptional B12 starting in adolescence achieved a better Vit.B12 and multi-micronutrient status in the offspring. The Vitamin B12 intervention group was found to perform better in the cognitive and language domains than the placebo control. Intriguingly, the Vitamin B12 intervention group also performed better than the group that received both Vit B12 and multiple-micronutrient supplementation.
An enviable biorepository spanning three generations in the PMNS study has been established, which is ready for multiple possible investigations in future (DNA, RNA, blood plasma and serum, urine and multi-site microbiome).
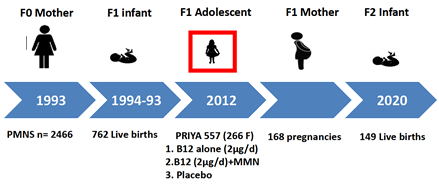
Figure 4: Pune Maternal Nutrition Study (PMNS) & Pune Rural Intervention in Young Adolescents (PRIYA)
5. Placental Biology
Placenta is one of the most important organs of human body, composed of both human and fetal tissue. Not only does it influence the maternal and fetal health during pregnancy, it has long term implications too. Placental insufficiency has been associated with several pregnancy related complications including preterm birth. In order to better understand this temporary but critical organ, major network programmes have been supported in the area of placental biology after completion of proof of principle studies for isolation of placenta derived nanovesicles. These nanovesicles provide a non-invasive window to the otherwise inaccessible placenta and determine fetal health and gestational outcomes. Efforts are also being made to identify real time molecular signatures of placenta during pregnancy using multi-omics approaches. Identification of these nodes could be used as diagnostic markers for monitoring the optimal placental functioning for healthy pregnancy, help triaging pregnant women at risk and manage them differently.
Transcriptome analysis of the placental exosomes isolated across different gestational stages of pregnancy indicates that there is a temporal regulation of gene expression of the genes involved in early embryonic development such as actin cytoskeleton organization, appropriate cell positioning, and B-cell regulation. Protein cargo analysis of these exosomes so far indicate the presence of 63 differently expressed proteins in term and preterm delivery mothers. The levels of one of these proteins, Human Leukocyte Antigen–G (HLA-G), which is expressed on the fetal-origin extra-villous trophoblasts (EVTs) and is a crucial factor towards establishment and maintenance of an immune-tolerant zone in the placenta for a healthy pregnancy outcome was higher during early pregnancy in mothers delivering SGA neonates. This may possibly be a mechanism to compensate for any adverse outcomes. Further detailed multi-omics analysis is expected to provide more exciting insights and possible identification of the molecular signatures of placenta during pregnancy.
6. Reproductive Biology
Infertility has become a pressing problem worldwide in the recent times affecting about 15% of the couples. One study in this area has revealed that alterations in HOXB1 expression correlates with male infertility, which may result from HOXB1 mediated changes in the signaling pathways important for spermatogenesis, particularly cell proliferation, differentiation and meiosis.
In an undergoing study on assisted reproductive technology (ART), it was noted that women of the ART group have a higher blood pressure and are in the older age group. Preliminary data indicates lower placental mRNA expression levels of angiogenic factors-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and placental growth factor (PlGF) in the ART group as compared to the non-ART group.
A preclinical study on the management of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), showed that treatment with 4-Hydroxy isolucine obtained from fenugreek seeds can significantly improve the ovulation potential /rate in rats, indicating a great potential of the natural product, 4-HIL in the management of PCOS.
New Initiatives
7. Sepsis related mortality in neonates in India: a multidisciplinary, multi-institutional research program for context specific solutions
India accounts for nearly 40% of global burden of sepsis-related deaths in newborns and is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity among infants. The high incidence and case fatality rate, unique pathogen profile, source of causative pathogens, alarmingly high rates of Anti-Microbial Resistance (AMR), and distinct lack of reliable point-of-care diagnostics make it imperative to understand the biology of neonatal sepsis in a more comprehensive manner and find context-specific solutions.
A multi-institutional and multidisciplinary network programme has thus been supported to further the understanding of the causative and confounding factors associated with neonatal sepsis, and towards reducing the burden of sepsis.
8. Problems associated with Women health
In the area of Problems associated with Women’s Health, projects have been supported in the broad domains of ovarian stimulation on ovarian pathophysiology, cost effective tools for noninvasive prenatal screening, post-menopausal disorders, osteoporosis and auto immune disorders specific to women.
9. Developmental disorders and diseases of infancy and early childhood
In the area of Developmental disorders and diseases of infancy and early childhood, projects have been supported in the broad domains of Chronic Malnutrition and Cognitive Development, Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), Birth Asphyxia, Hyperbilirubinemia and Hypothermia and Infections: Management in vulnerable groups and Congenital Heart Diseases (CHDs).
Publications (last 5 years)
| Year | No. of Publications |
|---|---|
| 2017-2018 | 6 |
| 2018-2019 | 12 |
| 2019-2020 | 18 |
| 2020-2021 | 24 |
| 2021-2022 | 13 |
Details of Technologies / products / Process Developed:
1. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for estimation of a panel of lysophosphatidylcholines in dried blood spots for screening of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.
2. Flow injection ionization-tandem mass spectrometry-based estimation of a panel of lysophosphatidylcholines in dried blood spots for screening of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.
The above two technologies are used as two-tier tests for screening and identifying X-Adrenoleukodystrophy in patients using dried blood spots.
Patents
1. Title: RNA profile of circulating placental-derived exosomes for monitoring placental health Date of Filling - July 14th, 2018
2. The outcome on 4 Hydroxyisoleucine (4-HIL) compound possessing enormous potential for the Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) management been filed for Indian Patent (202011002962) and discussion is going on with the pharmaceutical companies for the technology transfer to bring the benefit to the society.
Contacts Concerned Officer for more Information
| Programme Head | Dr. Anamika Gambhir, Scientist G |
|---|---|
| anamika[at]dbt[dot]nic[dot]in | |
| Phone No. | 011-24363665 |
| Programme Officer | Phone No. | |
|---|---|---|
| Dr. Rajesh Ghangal, Scientist D | rajesh[dot]ghangal[at]dbt[dot]nic[dot]in |



















