Biomedical Engineering
Overview
Biomedical engineering is a highly interdisciplinary area of research involving cross disciplinary knowledge from engineering and other quantitative sciences for unraveling the complexities of biological systems and provides cost-effective solutions for improved quality of life. With a priority to study emerging diseases, to manipulate/engineer genomes, develop transgenic systems and develop genome-based diagnostics, the department significantly contributes towards biomedical engineering field for development of affordable devices, diagnostics, bio composites, tissue engineering, biosensors etc.
Mandate
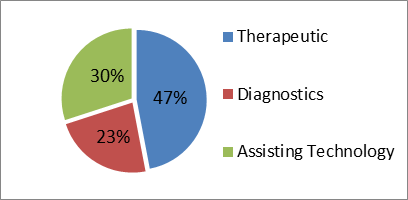
The mandate of the programme is “to promote multi-disciplinary research involving application of science and engineering for development of innovative technologies and products leading to affordable healthcare”. Major focus areas can be categorized as follows: a) Diagnostics - Bio sensors, in-vitro diagnostics, medical imaging, home care, wearables b) Therapeutics - Drug delivery vehicles, implants, tissue engineering, surgical robotics. c) Assistive technologies - Mobility aids, prosthesis, patient rehabilitation systems currently 47% of projects have been sanctioned under Therapeutics, 30% under Assistive technologies and 23% under diagnostics. In current year 10 new projects have been supported so far.
Achievements
| No. of research publication during 2021-22 | 15 |
| No. of patent applied | 8 |
| No. of patent granted | 3 |
| No. of human resource trained | 66 |
Success Stories
- A novel mechanical nitinol-based clot retriever has been developed through research efforts at Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences & Technology Trivandrum. Designing of computer model & Structural analysis has been done and two novel concepts of braided stent retrievers have been developed. The two braided concepts (continuous and segmented) have been prototyped. A total of 34 samples have been produced till date which involves a variation of the two braided concepts and 3 different diameter wires (80um, 100um, 150um). The device is expected to be used in the treatment of acute cerebral ischemic stroke.
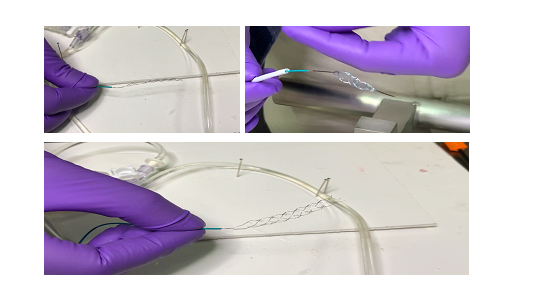
Comparison of Expansion of stent (continuous and segmented) after retrieval process
- In one collaborative project ongoing at Dr. Reddy's Institute of Life Sciences Hyderabad and University of Hyderabad a technology has been developed for manufacturing of microneedles (MNs) with prototype ready in small scale. The product is expected to address the specific problems in existing intervention strategies for iron and vitamin B12 deficiency without involving skilled personnel, infrastructure or significant investment. The product has the potential to impact the iron and vitamin B12 status of ~17 (170 million) crore Indian women of reproductive age and ~48 Crore (480 million) children annually.
-

Artificial Skin model after piercing with microneedles with Hyaluronic Acid Tip (hard needles, no bending during piercing, holes made in full length)
- In other ongoing collaborative study at IIT Hyderabad, LVPEI Hyderabad and CCMB Hyderabad for 3D Bioprinting and remodeling of corneal stroma and epithelium for Keratoplasty, it was found that dCMH has many advantages over existing materials including easy availability, simple formulation procedures, biocompatibility and it can prevent the trans-differentiation of corneal stromal keratocytes to myofibroblasts in vitro which make it a promising material for prophylaxis against blinding scar formation in an injured cornea. Unlike the biomimetic materials reported earlier for corneal tissue engineering, a completely biological matrix was introduced with the ability to prevent corneal scarring. As discarded corneas were used for this study and earlier reports have successfully described the application of other xenogeneic decellularized tissues in humans, this could be a future prophylactic strategy which is reliable and clinically feasible to prevent corneal scarring and thereby save vision
- A study for developing Functional Skin Construct with Embedded Pericytes is also supported at IIEST Shibpur and IIT Khragpur.
- In a study supported at NIT Surat a compact, lightweight, robust and stable wearable sensor device under conformal condition for knee effusion detection is being designed.
- In other study supported at CMC Vellore final version of non- invasive method for measuring beat-to-beat blood pressure variability in humans (CMC NIBP) has been built which is working to satisfaction level. It is used to generate blood pressure data. An ultrasound-based method for measuring volume flow in ml/s has been developed. A method to estimate resistance and capacitance from pressure and flow has been developed. It has been ascertained that resistance changes occur at the level of small arteries and capacitance changes occur at the level of large arteries. These methods will be employed to redefine action of vasoactive drugs whether they act on small arteries/ large arteries or both. The information generated will help redefine therapeutics in diseases like hypertension.

- Technological development of Multi-wavelength Selective Plane Illumination Microscope (mλSPIM) imaging system – with simultaneous magnification at multiple levels is successfully accomplished at IISER Trivandrum. Validation studies were carried out with various biological specimen including zebrafish, HeLa cells, mouse embryo, drosophila brain, and HeLa Kyto cells where various fluorescence dyes of different optical excitation wavelengths were tagged to the specimen. The unique features of sMX-SPIM hold promises to observe and study (i) sub-microscopic details and entire structure of biological specimen side-by-side simultaneously, (ii) spatio-temporal dynamics of functional activities of biological specimen.
- Under a project supported at Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Coimbatore for paper based microfluidic chip for the monitoring of women health after 40 a highly sensitive device for the quantification of the biomarkers for liver function test based on colour intensity has been developed.
- During the year a non- invasive method for measuring beat-to-beat blood pressure variability in humans (CMC NIBP) and a clot retriever stent have been developed.
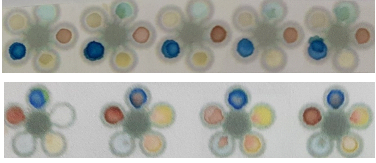
Response of the paper strip with different blood samples
- In a project implemented at IISc Bangalore Fluorescence based rapid optical volume screening system (OVSS) for interrogating multicellular organisms has been developed. The Fastest Volume Imaging System which reduces the data acquisition time by almost 10 times as compared to standard Lightsheet System. This system is capable of simultaneous screening of multiple organs during its development. The illumination system generates multicolor Lightsheet and has been tested on standard test sample. Present testing is going on Zebrafish embryo.
- Recently Centre of Excellence (CoE) project for bioengineering has been completed successfully. Under this three studies were supported for (i) development of acetabular cup for hip replacement, (ii) femoral head, and (iii) dental implant, with multiple objectives. In project 1, Acetabular socket prototype for hip implants with dimensions especially suited for Indian patients has been developed at CIPET Chennai and HIP simulator study on acetabular socket was carried out at CGCRI, Kolkata. While, its in vitro toxicity analysis of wear debris is being carried out at IISc Bangalore. In project 2, quality assessment of patientspecific Zirconia toughened Alumina based femoral ball head manufactured at two different institutes via 2 techniques has been done. In project 3, CAD based model for tooth replacement has been developed and the implant was fabricated using 3D printing technology. It’s in vitro assessment of the cytocompatibility properties was also performed. A prototype of ceramic coated dental implants using state-of-art coating deposition techniques has been developed and pre-clinical tests in animal models involving histopathologist are going on. This center has developed patient-specific implants for musculoskeletal reconstruction, using conventional and additive manufacturing techniques. So far 32 publications, 4 patent filing, one patent granted and one technology has been transferred under this CoE project.
DBT BIODESIGN PROGRAM
The Biodesign program of the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) was pioneered by the visionary formed DBT secretary late Dr M.K. Bhan in the Year 2008 to ignite the then nascent med-tech ecosystem in the country. DBT has set up 4 different centers across the country.
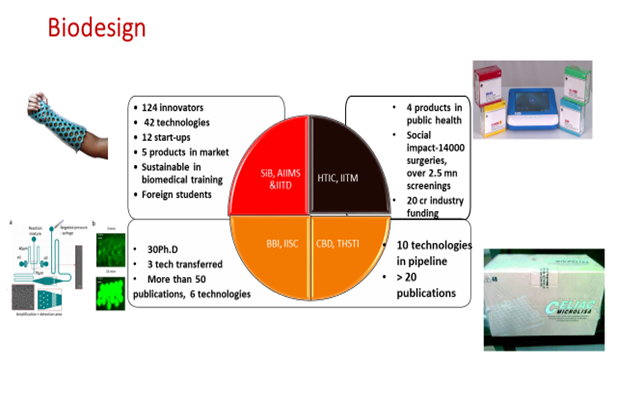
- DBT initiated this as a fellowship program jointly at AIIMS and IITD with clinical immersion in India and biomedical training in Standford. The program has become self-sustainable in terms of the biomedical training since 2014 as the training is indigenously provided and fellows from other countries like Australia, Japan are visiting India for this program. The program has achieved acclaim and impact right from capacity-building to commercialization of products. 124 fellows and interns have been trained, 42 technologies developed, 22 licensed, 12 start-ups formed in the area of work & 10 more in related domains, 5 products have been commercially launched. More importantly when we tracked the career paths of the trained fellows 90% of them continued their career paths in the med-tech ecosystem.
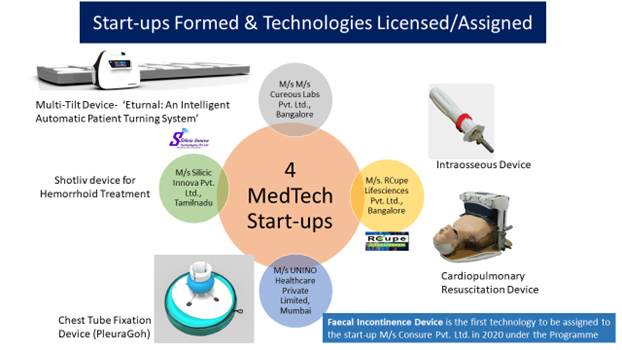
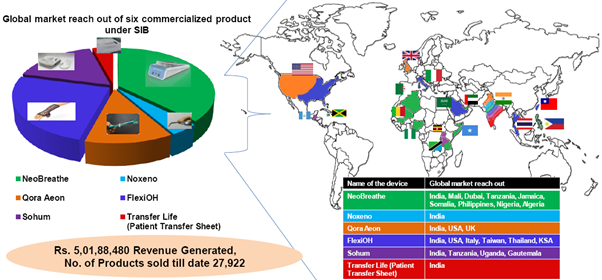
- The second center was at IIT Madras research park with IIT M faculty participating with clinicians in and around the region. This followed a Harvard Model wherein the clinical need is identified by the physician and the IITM faculty with expertise in systems engineering designed and built products. The salient achievement has been deploying of these products into public-health and patientcare delivery channels and attracting huge industry funding. Four products have been launched for public health care and has enabled in impacting lives of millions in performing on-site surgeries and assessments. The center has grown form 4000 sq.ft to 12,000 sq.ft space with dedicated med-tech incubation.
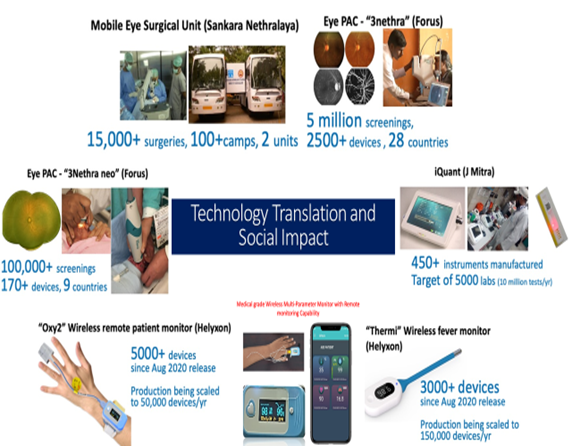
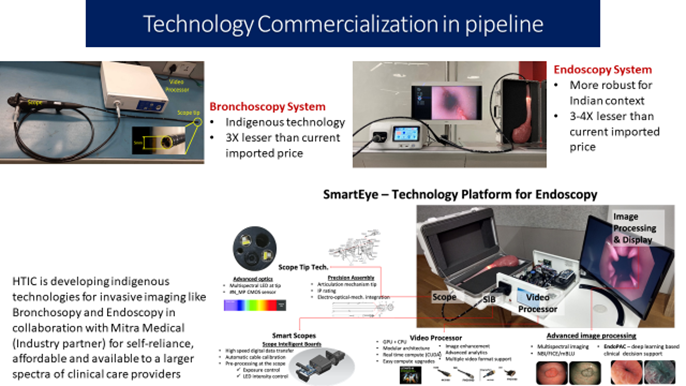
- The third center at IISC Bangalore in collaboration with hospitals around Bangalore has helped in championing the new generation leadership in this interdisciplinary domain with about 30 research students pursuing Ph.D. Products developed have been licensed to start-ups for further development. What was initiated as a project by DBT has now emerged as a new, key research center of the institute. Many faculty from IITs have joined the center. Along with CMC, Vellore, jointly-supervised MD-PhD programme is being implemented. In addition to capacity-building, a number of publications and research leads has emerged from this initiative.

- The fourth center at translational Health Science and technology institute (THSTI), Faridabad adopted biodesign for translational biomedical research with a thrust focus on in-vitro diagnostics. Numerous national and international collaborations have been forged and a state-of-art support infrastructure has been created. All these has helped in expanding capacity-building for healthcare innovation in India. The “mission critical centre” of the institute hasa pipeline of diagnostic products at different stages of development with a number of research articles and patents on these.
NEW INITIATIVES
Based on the success of these centers DBT at present aims to nurture more Schools of Innovation in Biodesign (SiB). A grant announcement has been made in this regard. The purpose is to derisk the entrepreneurial journey of the aspiring med-tech innovators as well as to offer solutions for the import-driven India’s public healthcare technology needs through mutual collaborations amongst committed organizations.

Five New Biodesign centers twinning medical and engineering institutes have been identified through national call
- KGMU Lucknow & IIT Kanpur
- THSTI, CMC Vellore, PGIMER Chandigarh & IIT Madras
- IIT Guwahati, NEIGRIHMS, Guwahati Medical College
- IIT Bombay, Hinduja Hospital Bombay
- IIT Jodhpur & AIIMS Jodhpur
Make-in-India (MII)
Overview and Mandate
Make in India (MII) initiative was launched in 2014 by the Hon’ble Prime Minister of India. The initiative aims to encourage companies to manufacture their products in India, for India and for the world. Since its launch, the initiative has gained recognition and appreciation at societal, national and international levels. Make in India mission has introduced and prioritized multiple initiatives including Startup India to promote innovation, capacity building; strategic growth in Industrial sector, foreign direct investment promotion for technology adoption and manufacturing, Intellectual Property rights, employment generation and others.
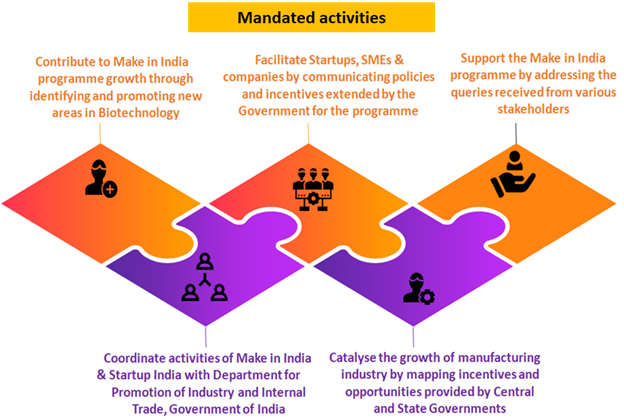
Major Programs and initiatives
- Aligned with the Make In India mandate, the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) under Make In India 1.0 had established a Make in India Facilitation cell at its public sector enterprise, Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) in 2015-16 initially for 3 years (106- 108/c). Subsequently, it was extended by another 3 Years i.e. 2018-2021 at a total budget of Rs. 267.456 lakhs. Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) through DBT regularly monitored the performance of Biotech sector through this Facilitation Cell at BIRAC. MII Cell at BIRAC successfully performed the mandated activities. Amongst the 25 sectors peers, Biotech sector activities have been appreciated acknowledging this sector’s growth potential.
- Meanwhile, Make In India 2.0 action plan was rolled out with revised and higher order expected deliverables from the biotechnology sector. Several of such new initiatives have already been undertaken by the Make In India cell, BIRAC such as Global Bio-India, Mapping India’s Bioeconomy, State Connect etc. So, to ensure continued support to the MII cell at BIRAC, the proposal was extended w.e.f. 20th August, 2021 till 31st March, 2022 after the approval from the competent authority
- Recently, Ministry of Commerce and Industry’s Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) – the reporting ministry for Make In India and Startup India national mission programs - have issued directions to DBT for establishment of a Project Development Cell (PDC) and an Investment Clearance Cell (ICC) - high priority, new activities of national significance. DBT has delegated MII cell at BIRAC to undertake these important new activities. So, one year extension to “Make in India” Facilitation Cell (MIFC) has been provided w.e.f. 01st April, 2022 to 31st March, 2023.
Achievements
| Schemes | FY 2021-22 | |
| Physical Targets | Achievements | |
| Make-in-India (MII) | Promoting Biotech Startups | 4800 |
| Establishing Biotech Incubators | 60 | |
| Support to Biotech Product development | 350+ | |
| Establishment of Regional Centres | 4 | |
| Establishment of Technology Transfer Offices | 7 | |
| Setting of Bio-connect offices | 5 | |

Contacts Concerned Officer for more Information
| Programme Head | Dr. Alka Sharma, Scientist H |
|---|---|
| alka[at]dbt[dot]nic[dot]in | |
| Phone No. | 011-24363699 |
| Programme Officer | Phone No. | |
|---|---|---|
| Dr. Kalaivani Ganesan, Scientist F | k[dot]ganesan[at]nic[dot]in | 011-24365321 |
| Dr. Abhishek Kumar Mehta, Scientist D | ak[dot]mehta[at]dbt[dot]nic[dot]in |
















