OVERVIEW
India is the largest animal husbandry sector in the world with largest livestock population to supports the livelihoods of more than two-thirds of the rural population, mainly small and marginal farmers. Livestock can sustain the food demands of the rural households and also provides stability at the time of crop failures. Therefore, sustainable animal production and health is important as healthy animals are closely related to healthy people and healthy environment. Livestock and Animal Biotechnology Decision Unit focus towards developing newer techniques/ technologies to enhance livestock production and productivity. R&D projects are being supported in the applied areas of animal reproduction, development of transgenic animal, genome and genetic characterization of indigenous breeds, animal nutrition, development of novel livestock by-products, development of animal vaccines and diagnostics, development of therapeutics, technology for bovine sperm sexing, production of bio- pharmaceuticals through transgenesis etc.
MANDATE AND THRUST AREAS
The mandate of this Division is the sustainable growth of livestock for nutritional security and economic prosperity as well as enhances production and productivity through biotechnological interventions.
- To establish collaborative research for development of new generation vaccines and diagnostics along with translation of existing candidate vaccines and diagnostics for field use around major animal disease of national importance to make product affordable to small and marginal farmers.
- To provide R&D support for generation of new knowledge in the priority areas livestock production and to develop skill pool to meet R&D requirements of the sector.
- To enhance production and productivity of livestock sector through biotechnological interventions in nutrition, breeding, genetics and by-products etc.
- To achieve excellence in innovation, technology generation for enhancing animal production in the country.
- To implement ‘ONE HEALTH’ research platform to address issues related to mitigation of existing and emerging zoonotic diseases
- To conduct basic and applied research in the area of nutrition using physiological and nutritional approach
NEW INITIATIVES
- Network Programme for ‘Bovine Sexed Semen Sorting Technology (BSSST)’
- PAN India network program on Canine Health Research - Phase II
MAJOR PROGRAMS
- One Health Initiative: Department has established a “One Health Center” at National Institute of Animal Biotechnology (NIAB), Hyderabad for inter-sectoral collaboration among veterinary, medical, agricultural, environmental, forestry, meteorological and other areas to detect, prevent and control zoonoses and transboundary animal diseases. Further, a mega-project “Establishment of a Consortium for One Health to address Zoonotic and Transboundary Diseases in India, including the Northeast Region” consisting of 28 organizations led by DBT-National Institute of Animal Biotechnology, Hyderabad has been supported. The One health consortium consists of AIIMS, Delhi, AIIMS Jodhpur, IVRI, Bareilly, GADVASU, Ludhiana, TANUVAS, Chennai, MAFSU, Nagpur, Assam agricultural and veterinary university and many more ICAR, ICMR centres and wild life agencies. This programme envisages carrying out surveillance of important bacterial, viral and parasitic infections of zoonotic as well as transboundary pathogens in India, including the North-eastern part of the country. The consortium designed sampling strategy, and finalized the assays, kits and standard operating procedures (SOP). Meta-analysis of existing literature was carried out to design the sampling frame for various species of animals, and hospital-based syndromic approach was used for humans. About 12,000 animal samples, around 3000 food-related samples, 650 wildlife samples and more than 5000 human samples have been collected and tested.
- Translational Research Platform for Veterinary Biologicals (TRPVB):TRPVB is a partnership initiative between the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) and TANUVAS-Chennai, to facilitate a collaborative and coordinated approach for the translation of technologies in the area of veterinary vaccines and diagnostics. Several universities and research institutions are performing research on the development of animal vaccines and diagnostics, but very few products have been commercialized in this sector. TRPVB was created with the vision to foster 'Productization' in the field of Veterinary Biologicals by converging the presently distant academic research, industry and pathways of regulatory compliance. TRPVB works towards to achieve the mission of translating of veterinary vaccines, diagnostics and other Biologicals for field application and harness their benefit to improve animal health and productivity thereby augmenting the economic status of farmers. Over the past more than 12 years, TRPVB has become a centre of reference to strengthen national, regional and international linkage and collaboration for animal vaccine and diagnostics development, exchange of materials, technology assessment, regulation, and knowledge sharing to support training, consultation and commercialization of technologies.
- Network Programme on Anthrax Diagnosis and Control in India: A network programme on ‘Anthrax Diagnosis and Control in India’ has been supported by the department to provide a multi-disciplinary research consortium with involvement of 10 partnering Institutes/Universities to strengthen the competences for surveillance, outbreak investigation, laboratory capacity, vaccination, specific predictors of outbreak risk and risk mapping. A ‘latex agglutination test for detection of B. anthracis spores in animal feed supplements and soil samples’ and a ‘portable UV aluminum cabinet for inactivation of B. anthracis spores in the soil’ have been developed in this project and are under validation stage. Whole genome sequencing and comparative analysis of 17 isolates from several animals (e.g., sheep, cattle, pigs, deer, goat, and contaminated soil sample) infected with B. anthracis has also be completed. Further, cryopreservation and molecular characterization of 23 isolates of B. anthracis obtained from different infected sites in India has also been done. Transgenic sorghum and rice plants have been successfully generated for the gene encoding for the domain IV of protective antigen and cholera toxin B subunit.
- Bovine Sexed Semen Sorting Technology: Department conducted a Brain storming meeting on ‘Bovine sexed semen sorting technology’ and reviewed the current status of research leads developed in this area and identified new research area for the development of indigenous technology. Further, based on this Brain storming meeting, Department constituted an Interdisciplinary Group of Expert and formulated a Call for Proposal on “Bovine Sexed Semen Sorting Technology (BSSST)” and three consortia projects have been supported using different approaches viz Aptamer and protein targeted approaches for sex specific spermatozoa enrichment in Bovines; Integrated Magneto-Acousto-Dielectrophoresis based microfluidics for the sorting of Bovine spermatozoa; and redesigning of FACS instrument for sorting Bovine Spermatozoa.
- Canine Health Research: Dogs are the true companions of human since antiquity however, funding for canine health Research has been given a least priority. Even, Hon’ble Prime Minister of India has emphasized a need to research on indigenous dog breeds of India. Department supported two major PAN India Network programmes at Tamil Nadu Veterinary and Animal Sciences University (TANUVAS) Chennai, Tamil Nadu and Guru Angad Dev Veterinary and Animal Sciences University (GADVASU), Ludhiana, Punjab. The major research purpose of these programs was on canine haemoprotozoan parasites, oncology, canine blood typing, canine enteric virus, canine contraception, canine ocular disorders and canine leptospirosis. In phase-I, outstanding research leads were generated, thereafter, keeping in view the outcomes of phase-I, DBT supported its Phase-II program for validation and commercialization of technologies/Products/Protocols/Feed developed during phase-I.
KEY ACHIEVEMENTS AND SUCCESS STORIES
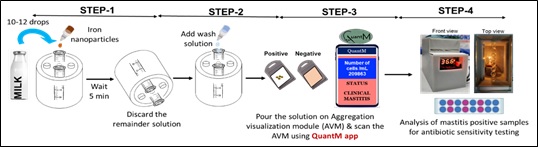
- Nanostructured paper-kit comprising magnetic nanoparticle for rapid detection of subclinical and clinical mastitis: An early detection of mastitis at subclinical stage holds high prognostic value as starting the medication at an early stage leads to rapid cure of the condition. NIAB- Hyderabad has developed and validated a field level, affordable, farmer friendly quantitative method to diagnose intra-mammary infection as well as subclinical mastitis (Limit of visual detection: 25,000 cells/ml of milk). Further, a technology has also been developed to perform on-field anti-microbial sensitivity testing within 2 hours’ time under field condition. Both the assays doesn’t require any trained personnel for performing as well as interpreting the assay results and it can be performed at the door step and under field conditions. These technologies have been transferred to ACS Neoteric Technologies LLP Hyderabad for commercialization.
- Subviral Particle Based Infectious Bursal Disease Vaccine: A technology named “Subviral Particle Based Infectious Bursal Disease Vaccine” intended for use against IBD also known as Gumboro disease of poultry, which was developed with the funding support of Department of Biotechnology has been transferred to M/s. Hester Biosciences, Ahmedabad on 28.02.2024 by IVRI- Bareilly and Agrinnovate (AgIn), New Delhi. The SVP based vaccine completely protects the broiler birds in presence of maternally derived antibodies (MDA) and can safely be administered to day-old chicks. The vaccine does not cause immunosuppression as has been demonstrated by an intact histological architecture of the bursa of Fabricius in immunized birds.

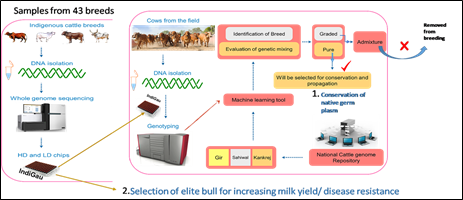
- Genomics for conservation of indigenous cattle breeds and for enhancing milk yield:The Department supported a program for the development of high density single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) chip for identification of pure indigenous cattle breed as well as elite animal at National Institute of Animal Biotechnology (NIAB), Hyderabad. Through this project, genotyping and sequencing of the 43 indigenous registered cattle breeds including five major cattle breeds - Gir, Tharparkar, Kankrej, Red Sindhi and Sahiwal were performed. The Chip named as IndiGau which is the largest cattle chip of the world. It has 11,496 markers (SNPs). This is the first chip developed for Bos indicus (Indian breeds). Further, India’s first SNP based chip for the conservation of pure varieties of indigenous cattle breeds has been released by Dr. Jitendra Singh, Hon’ble Minister of State (IC), M/o S& T on 13th August 2021.
- Early pregnancy diagnosis in cattle and buffalo:The Preg-D kit, the prototype of a urine based novel technique for pregnancy diagnosis in dairy animals has been developed with support of DBT at the ICAR-Central Institute for Research on Buffaloes, Hisar. This innovative kit employs a thermophilic biochemical reaction to detect metabolites, resulting in the formation of a coloured precipitated compound in positive cases. The kit will preliminarily diagnose the pregnancy as early as day 18-25 in bovines. It does not require any instrumentation and results can be interpret by naked eye. It does not require any instrumentation and results can be interpret by naked eye as well as the kit is non-invasive, cost-effectiveness, user-friendly and animal-friendly.

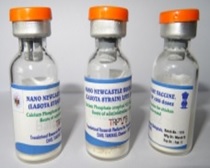
- Nano-Newcastle disease virus vaccine: Newcastle disease is a highly contagious disease of birds caused by a para-myxo virus. TRPVB at TANUVAS- Chennai has developed a Nano based Newcastle disease virus vaccine. This is the first nanotechnology-based vaccine of our country that has been licensed for commercial production and use in chickens. This technology has showcased the benefits of nanotechnology applications in vaccine delivery systems. This reiterates that successful ‘productization’ is possible through active academia-industry-funding agency linkage and is a testimony to Aatma- Nirbhar Bharat. The advantages of this vaccine are two-fold. The vaccine is effective at 100-times lower dose than conventional (non-nano) vaccine. This implies that 100 times more doses can be manufactured with the same volume of virus-infective fluids than conventional vaccines. Further this nano vaccine is found to be more effective in the face of maternal antibodies while the conventional live vaccines would get neutralized by them. The technology of nano Newcastle disease virus vaccine production has been transferred to M/s. Hester Biosciences Limited, Ahmedabad. The recipient company, after complying with all the regulatory processes, has received manufacturing license for the Newcastle disease vaccine Live Nano for both domestic use and export purpose.
- Brucella delta S 19 vaccine: Department has successfully completed a network programme on bovine brucellosis in which an improved brucella vaccine viz. modified delta S 19 vaccine has been developed. Safety and potency of delta S 19 vaccine has been done in mice model and also evaluated successfully in buffalo. Delta S19 vaccine is more safe in comparison of existing vaccine without any side effect. The technology of Brucella abortus S19∆per vaccine has been transferred to M/S Hester Biosciences ltd on 22nd September, 2020 for commercialization.
- Embryo transfer technology: The department supported a mission mode programme to enhance the productivity of livestock and emphasis was given on standardization of various techniques of Embryo transfer technology (ETT). The technology was successfully standardized in cattle, buffalo, goat, equine, camel, mithun and yak. The department established three main ETT centre and 14 regional ET labs in different parts of the country. Various techniques viz. super ovulation, in vitro culture of embryos, embryos transfer etc. were standardized. ETT demonstration activities were undertaken at the farmers level and a number of cattle and buffalo calves were produced. With the help of ETT an intensive selection among male and female livestock can be carried out in elite herd at an early age using the family information and thus reduce the generation interval and bring about desired change in short span of time.
- Open nucleus breeding system:The department initiated Open nucleus breeding system (ONBS) for enhancing the productivity of Sahiwal and crossbred Sahiwal cattle at National Dairy Development Board (NDDB), Anand. The nucleus was established from the best animals obtained by screening the base population. During the project duration, 268 male calves and 259 female calves were produced through embryo transfer. This programme was adopted by NDDB, Anand for continuous production of male Sahiwal and crossbred males for National Artificial Insemination programme.
- Genetic Improvement: Genetic improvement of local sheep breed of Kashmir and Maharasthra using Fec B mutation and their genetic characterization were carried out successfully. Approximate 45% more lambs were produced by the heterozygous ewes having Fec B mutation whereas homozygous ewes gave birth to 65.5% more lambs than non carries ewes. The study confirmed two distinct groups among FecB carrier crossbred ewes with low and high average litter size. Department of Animal Husbandry, Govt. of India has adopted this programme and a national programme on genetic improvement of sheep breeds was launched.
DETAILS OF KEY TECHNOLOGIES/PRODUCTS/PROCESSES TRANSFERRED TO INDUSTRIES: Click Here to View
Contacts Concerned Officer for more Information
| Programme Head | Dr. Nitin Kumar Jain, Scientist G |
|---|---|
| nitink[dot]jain[at]nic[dot]in | |
| Phone No. | 011-24365972 |
| Programme Officer | Phone No. | |
|---|---|---|
| Dr. Manish Rana, Scientist F | manish[dot]rana[at]nic[dot]in | 011-24363012 |
| Dr. Lokesh Kumar Narnoliya, Scientist D | lokesh[dot]narnoliya[at]dbt[dot]nic[dot]in | 011-24360295 |